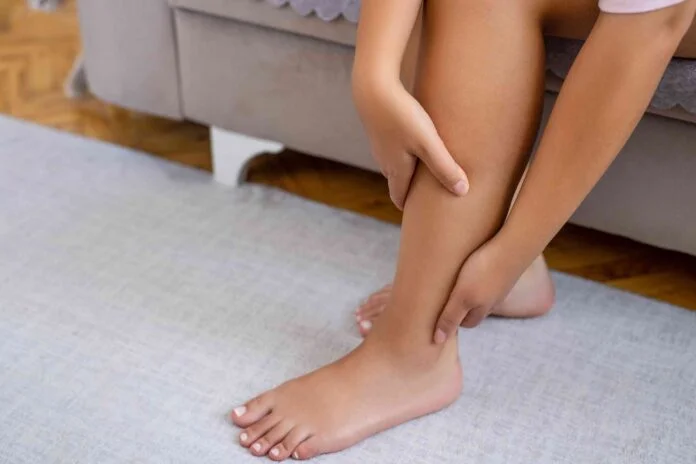
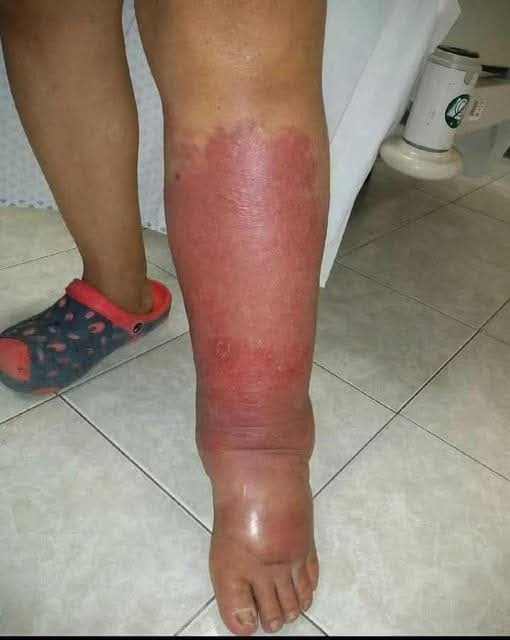
Believe it or not, my pitting edema was so bad that I could press on my ankle and leave a perceptible dent.
I wasn’t very old then. I wasn’t taking any drugs. But I didn’t know it yet; something was extremely wrong.
In earlier images, my face seemed round and almost puffy. At the time, I didn’t know that this was more than just a cosmetic issue. If your face looks bloated and puffy, it could be a sign that your blood sugar is too high. Those blood sugar difficulties produced a lot of health problems for me, like my legs and ankles swelling all the time.
If your lower legs, ankles, or feet are swollen, you should be worried. This is edema. You might have been told that you have a heart problem, a liver problem, a kidney condition, or that you eat too much salt. Those things can be reasons, but I’ve found that there’s a much more prevalent cause, and the good news is that it’s easy to fix.
Let me tell you what’s going on in your body and how to repair it quickly, safely, and without using any harmful medicines or diuretics.
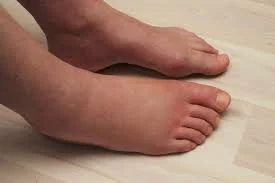
What is edema to begin with?
Edema is when fluid becomes stuck in your body’s tissues, generally in your lower legs, feet, or ankles, and causes swelling. It can hurt, feel heavy, or be tight. And in really bad cases, pressure on the skin might leave a dent that lasts (pitting).
Some of the explanations people provide online are:
Heart failure
Kidney problems
Liver disease
Too much sodium
A few drugs
But there’s another component that not many people (not even doctors) think about…
Inside your body, each of your cells has tiny systems that help them control fluids, especially the sodium-potassium pump.
These small pumps are all throughout your body. They move sodium out of the cell and potassium in, which keeps the right quantity of fluid inside and outside the cell. When these pumps cease operating, fluid spills out and collects in the spaces between your cells. This is what causes your ankles and legs to swell.
Imagine what would happen if the sump pump in your basement stopped working and water started to flood in. When these sodium-potassium pumps quit operating, this is what occurs inside cells.
And here’s why they don’t work: you eat too much sugar.
High blood sugar, glycation, and edema.
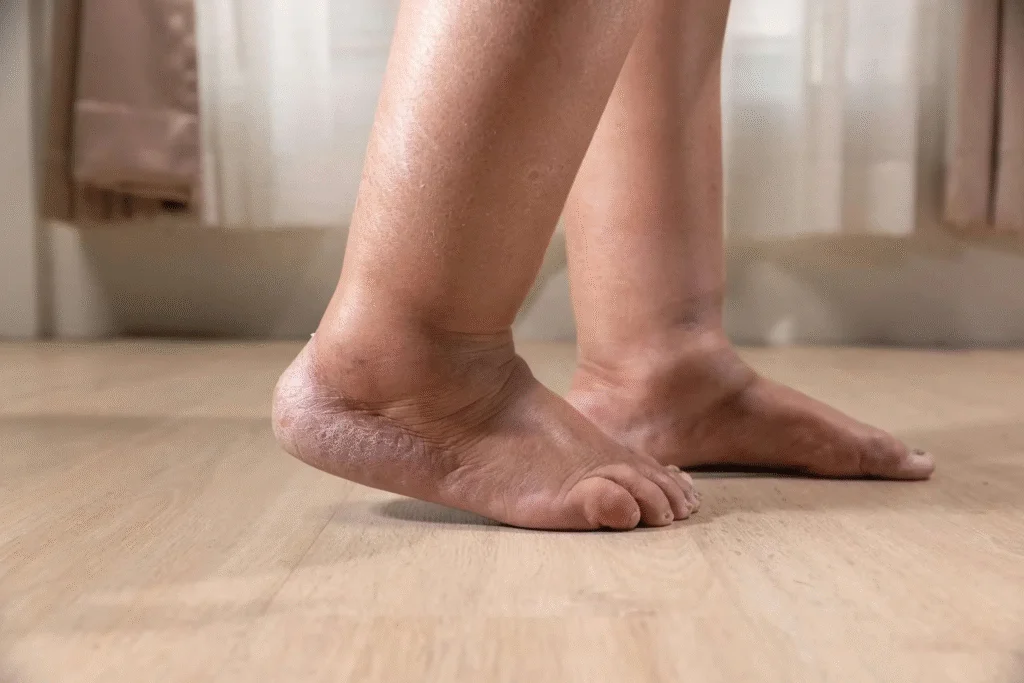

Eating refined carbs or sweets raises your blood sugar levels. That sugar doesn’t just sit there; it does things. It attaches to proteins in your blood, like hemoglobin, which is the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
This process of binding is called glycation.
When sugar molecules cling to proteins in the blood, this is called glycation.
The A1C test looks for this. A1C is a three-month average of how much sugar is “stuck” to your blood cells.
Sugar sticks to the proteins in your blood and doesn’t come off. It stays there until the red blood cell dies, which takes roughly three months. This buildup makes it difficult for blood to flow, affects your circulation, and makes it harder for nutrients to reach where they need to go.
Because of that bad circulation, fluid builds up in your lower body, especially in your feet and ankles. It also causes your blood vessels to leak, which lets fluid seep into nearby tissues.
More Sugar implies… More Swelling
Eating more refined carbs makes your blood sugar level higher and causes greater glycation. Over time:
The blood doesn’t do a good job of getting oxygen and nutrients to the body.
Things start to leak fluid.
The edema in the feet and legs gets worse.
Your nerves start to break down, which can make your feet feel numb, tingle, or burn. This is called peripheral neuropathy.
This process could already be damaging you if you eat a lot of carbs, are borderline or prediabetic, or aren’t legally “diabetic.”
That was me. I didn’t know I had a problem until I started to show indicators of it.
The Three Most Important Nutrients That Can Help
We need to fix the sodium-potassium pump in your cells to get rid of the swelling. To do that, your body needs three important nutrients:
1.Potassium
Potassium is crucial for keeping fluids in balance and for the nerves to work right. This mineral is also used the most by the sodium-potassium pump. But you need a lot of potassium every day—about 4,700 milligrams. And most people don’t even come close. Let’s break that down: There are roughly 300 milligrams of potassium in a banana.
You’d have to eat more than 15 bananas a day to accomplish your target, which is too much sugar.
Better sources of potassium are: Avocados with leafy greens, such spinach and kale
Fruits
Electrolyte powders without sugar
2.Magnesium
Potassium and magnesium work together to generate ATP, which is the main energy molecule in your body. It is crucial for: Loosening the muscles
Reducing cramps
Helping the blood move
Providing the sodium-potassium pump with the energy it needs
You just need 400 to 420 mg a day, but most people don’t receive enough. Magnesium can be found in a number of good places, such as Pumpkin seeds
Sunflower seeds
Leaves of greens
Almonds
Supplements that are of good quality (keep away from those with extra ingredients)
3.Vitamin B1 (Thiamine) is the most important supplement for stopping edema caused by sugar damage. Vitamin B1 helps your body use carbs. Without it, you can’t transform sugar into energy. Instead, sugar builds up and makes glycation happen. When you don’t get enough B1: Sugar thickens your blood.
Fluid leaks from vessels.
Pain starts in the nerves.
You might have trouble moving your hands and feet.
And the worst part is that sugar reduces your B1 levels. So, eating more carbs makes you less energetic, which makes the cycle worse.
The best places to get B1 are:
Nutritional yeast that doesn’t taste sweet
Sunflower seeds
Beef liver, asparagus, and B1 vitamins, especially benfotiamine, which the body can absorb more easily.
Stop the sugar and help the pumps.
This is what helped me, and it might help you too:
Step 1: Stop consuming sugar and refined carbs. This includes: Soda, juice
Pasta, bread, and cereal
Sweets and pastries
Snacks that have been changed in some way
The swelling started to go down in a few days after I stopped consuming these.
Step 2: Add extra magnesium, potassium, and B1. I used: An electrolyte powder without sugar that contains magnesium and potassium
Every day, eat nutritional yeast (for B1).
Benfotiamine is a B1 supplement.
Nuts, berries, leafy greens, and avocados
Within a week, my ankles looked smaller. After two weeks, the pitting was gone. My feet were also starting to feel better, and the tingling and numbness were going away.
One Last Thing About Staying Safe
If you start eating sugar and refined carbs again, the swelling will come back. The sodium-potassium pumps will break down again, and your body will start to hold onto water. This way of doing things isn’t about instant fixes. It’s about recognizing what your body needs to perform well and giving it what it needs.
Video 👇